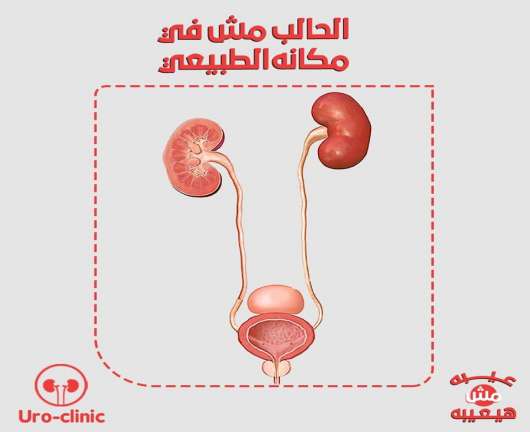
It is a medical condition in which the ureter does not end in its natural place in the bladder
It may be accompanied by abnormal kidney growth and frequent infections of the urinary system and urinary incontinence.
Ectopic ureter is found in 1 in 2000-4000 patients.
It is difficult to diagnose but often appears in a CT scan.
Prenatal may be detected by CT scan.
After childbirth, the symptoms are similar to those of a urinary tract infection, such as:
- High temperature.
Frequent urination.
Burning of urine
Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea
Treatment of ectopic ureter or (in the abnormal place):
1 - In the case of double ureter, which represents 80% of cases:
If the upper part of the kidney works well, the ureter can be implanted into the bladder.
- If the upper part of the kidney is atrophic, it will be removed by laparoscopy or surgery.
2- In the case of a single ureter and the opening outside the bladder:
- If the kidney is atrophic, it will be removed by laparoscopy or surgery.
If the kidney is working well, the ureter can be implanted into the bladder.